Introduction
In today’s digital landscape, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As technology advances, so do the threats that target our digital assets. Among the various areas of cybersecurity, image annotation has emerged as a crucial aspect in ensuring the integrity and security of visual data. This article explores the intersection between image annotation and cybersecurity, highlighting its significance, challenges, and potential solutions.
-
The Role of Image Annotation in Cybersecurity
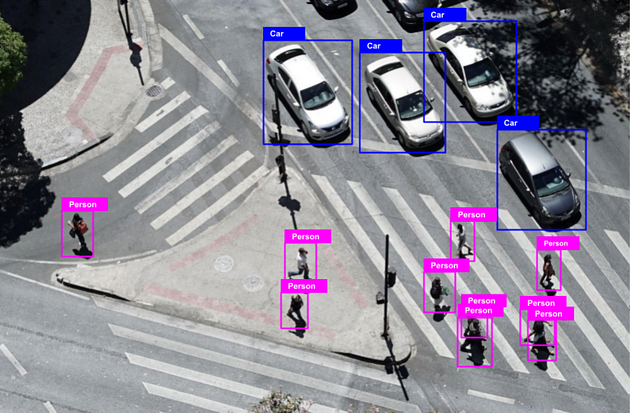
Image annotation involves labeling or tagging images with relevant metadata, such as objects, attributes, or regions of interest. This process serves multiple purposes in the realm of cybersecurity, including:
a) Threat Detection: Annotated images can be utilized to train machine learning algorithms for threat detection purposes. By categorizing and labeling images, cybersecurity systems can identify potential vulnerabilities or malicious activities within visual data.
b) Malware Detection: Image annotation can aid in the detection of malware embedded within image files. By analyzing the annotated metadata, security systems can identify suspicious patterns or hidden malicious code, preventing potential cybersecurity breaches.
c) Access Control: Annotated images can be used to enhance access control mechanisms by verifying the authenticity of individuals or objects. By associating annotations with authorized entities, security systems can ensure only authorized personnel gain access to sensitive information or restricted areas.
d) Forensic Analysis: In the event of a security breach or cybercrime, annotated images can provide valuable forensic evidence. By analyzing the annotations and associated metadata, investigators can reconstruct events, identify perpetrators, and gather critical information to strengthen cybersecurity defenses.
-
Challenges in Image Annotation for Cybersecurity
While image annotation plays a vital role in cybersecurity, several challenges exist in its implementation. Some of these challenges include:
a) Scale and Complexity: The scale and complexity of image datasets pose challenges in accurately and efficiently annotating vast amounts of visual data. With the exponential growth of data, manual annotation becomes impractical, requiring automated or semi-automated annotation techniques.
b) Quality and Consistency: The quality and consistency of annotations are crucial for reliable cybersecurity analysis. Inaccurate or inconsistent annotations can lead to false positives or negatives, compromising the effectiveness of cybersecurity systems. Ensuring high-quality annotations requires rigorous validation and quality assurance processes.
c) Adversarial Attacks: Adversarial attacks targeting image annotations pose a significant challenge in cybersecurity. Attackers can manipulate annotations to deceive or confuse security systems, leading to misclassification or the evasion of detection algorithms. Robust defenses against such attacks must be implemented to ensure the integrity and reliability of image annotation-based cybersecurity solutions.
d) Privacy and Ethical Considerations: Image annotation often involves handling sensitive or personal data. Balancing the need for accurate annotations with privacy and ethical considerations is crucial. Anonymization techniques, data protection measures, and adherence to ethical guidelines are essential to protect individuals’ privacy and maintain public trust.
-
Solutions and Best Practices
To overcome the challenges associated with image annotation in cybersecurity, the following solutions and best practices can be adopted:
a) Automation and AI-assisted Annotation: Leveraging automated or AI-assisted annotation tools can significantly improve efficiency and scalability. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to perform initial annotations, which can then be refined and validated by human annotators, striking a balance between speed and accuracy.
b) Quality Assurance and Validation: Implementing robust quality assurance and validation processes is vital to ensure the accuracy and consistency of annotations. Regular audits, inter-annotator agreement assessments, and feedback loops between annotators and domain experts can help maintain annotation quality standards.
c) Adversarial Defense Mechanisms: Developing defenses against adversarial attacks targeting image annotations is critical. Techniques such as robust machine learning models, adversarial training, and anomaly detection can help mitigate the impact of adversarial manipulations and enhance the resilience of cybersecurity systems.
d) Privacy and Ethics Compliance: Adhering to privacy regulations and ethical guidelines is paramount in image annotation for cybersecurity. Implementing privacy-preserving techniques, obtaining informed consent, and anonymizing sensitive data are crucial steps to ensure compliance and protect individuals’ privacy.
Conclusion
Image annotation plays a significant role in enhancing cybersecurity by enabling threat detection, malware analysis, access control, and forensic analysis. However, challenges such as scale, quality, adversarial attacks, and privacy considerations must be addressed to maximize the effectiveness and reliability of image annotation-based cybersecurity solutions. By adopting automation, ensuring quality assurance, implementing adversarial defense mechanisms, and complying with privacy regulations, organizations can harness the power of image annotation to bolster their cybersecurity defenses in an increasingly digital world. As Cyberatic Security, we are committed to providing cutting-edge image annotation solutions tailored to the unique cybersecurity challenges faced by our clients, safeguarding their digital assets and protecting them from evolving threats.